Syphilis

Treatment Duration
30
Suggested Sessions
2-3 times/year
What is Syphilis?
For many years the medical community considered syphilis to be a thing of the past. International epidemiological data show, however, that syphilis is back.
Syphilis is a mainly sexually transmitted disease, which develops in stages and presents many different symptoms. It affects both men and women and if not treated in time, it can cause serious damage.
The good news is that today it is possible to diagnose and treat syphilis.
It is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum and is characterized as "the great imitator", due to its frequent and atypical appearances.
Syphilis: Causes of Appearance
The bacterium Treponema pallidum is responsible for the appearance of syphilis.
The bacteria enter the body through the anus, vagina, penis, mouth or through cracks in the skin. Then they continue their action in the body, causing serious damage to vital organs.
Who does Syphilis affect?
Any sexually active person can develop syphilis, as the disease is transmitted through sexual contact.
There are risk factors, however, that favor the transmission of syphilis such as:
- Having sex with multiple partners without precautions.
- Sexual intercourse between men.
- Sexual intercourse without precautions.
- Infection with the virus that causes AIDS- HIV.
 «Syphilis makes the transmission of HIV easier»
«Syphilis makes the transmission of HIV easier»
Syphilis Transmission
Syphilis is a contagious disease, especially in the first and second stages. It is mainly transmitted by sexual intercourse, oral, vaginal and anal, even when there is no penetration or ejaculation. Syphilis can also be spread through contact with the wound or ulcer of someone who has syphilis.
It's worth noting that even when you don't have a rash or sores, you can still spread syphilis, as the infection remains in your body until you receive appropriate drug treatment.
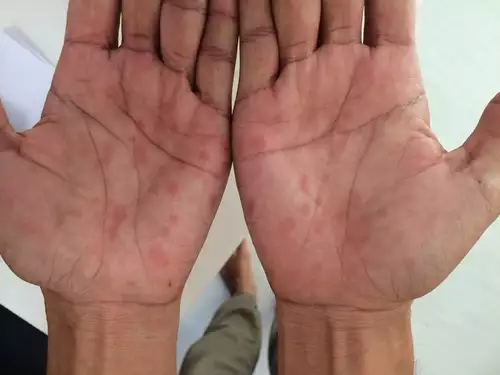
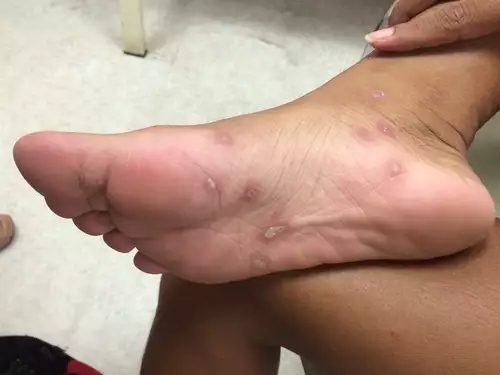
In addition, syphilis can also be transmitted from mother to child, during pregnancy or childbirth. It is called congenital syphilis and its treatment is mandatory since it can cause malformations in the child's skull such as in the nose and teeth as well as rashes on the soles and palms.
You will not get syphilis from:
- toilet seats
- pools
- jacuzzi
- showers
- sharing clothes or food
Syphilis Symptoms
Syphilis develops in stages, which are characterized by various symptoms, as well as by different transmissibility. The disease is highly contagious in the early stages, i.e. in the first and second stages.
In the third stage, syphilis is latent, that is hidden. This means that the infection is there, just that its symptoms are not visible. Medication is the only way to cure syphilis and stop its dangerous progression.
Syphilis: Photos
Syphilis Stages
The development of syphilis takes place in stages and the symptoms are different for each stage.
However, in some cases there may be an infection that does not show symptoms for many years or when the stages coincide the symptoms may appear in a different order.
Primary Syphilis
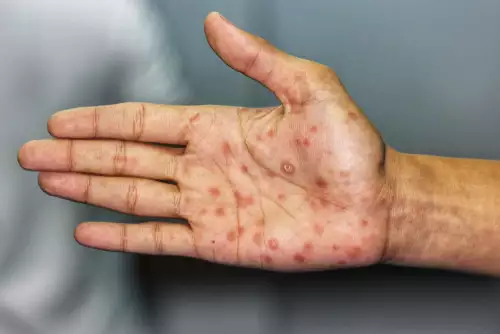
The main symptom in the first stage of syphilis is the syphilitic ulcer.
It is a wound usually small that does not itch or hurt. Most often, it appears at the point from where the bacteria entered, i.e. the genitals.
This sore usually appears three weeks after exposure to the disease, while many people will not notice it since it can be hidden in the vagina, rectum or mouth.
- inside the mouth (oropharynx, tongue)
- on the penis
- in the vagina
- in the anus
If left untreated, a syphilitic ulcer heals on its own in about six weeks.
The sores in syphilis heal on their own and pave the way for the second stage of the disease, which progresses if there is no treatment.
At this stage syphilis is highly contagious.
Secondary Syphilis
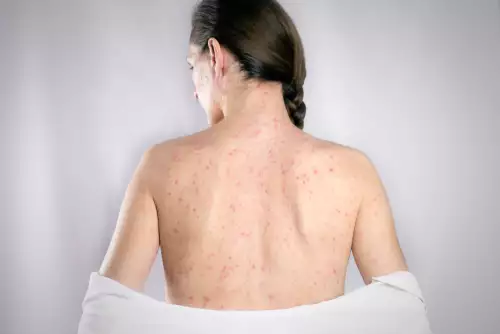
The second stage of syphilis begins after the initial sores have healed and within 6 months. At this stage the symptoms spread to the trunk, as well as to every part of the body even to the soles and palms.
In the second stage, rashes first appear on the trunk which may later spread to the rest of the body, the palms, the soles, and even the mouth, while there is a possibility that lesions that look like ants will follow. In addition, symptoms such as sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, muscle pain or fever may be observed.
In addition to skin manifestations, syphilis can also cause in the second stage:
- fever
- fatigue
- sore throat
- weakness
- hair loss
- weight loss
- swollen lymph nodes
These symptoms, if left untreated, are likely to resolve completely within a few weeks. However, there is a possibility of relapse and recurrence of symptoms in the next 12 months.
The second stage in syphilis can last from a few weeks to a few months, after which the symptoms will disappear.
At this stage syphilis is contagious.
Latent Syphilis
Syphilis at this stage has no symptoms. This particular stage may even last for several years. In this period the disease stops being contagious after some time.
In the latent stage of syphilis, which follows the first two stages, while you have no symptoms you are still spreading the disease. If you don't get treatment for syphilis you can stay in this stage for many years. Even for the rest of your life. It is also possible that the disease - syphilis will recur and you will again find yourself in the second stage and then return to its latent form again.
In this "silent" stage, syphilis is rarely transmitted.
In this period the disease stops being contagious after some time.
Tertiary Syphilis
Tertiary Syphilis is a stage that is not often encountered nowadays.
The third stage in syphilis is the most serious as syphilis can cause serious and irreversible problems in vital organs, such as the brain, nerves, eyes, heart and blood vessels. These problems are estimated to occur in 15 to 30% of patients who do not receive treatment for syphilis, usually several years (up to 30 years) after infection.
If you do not receive treatment and the infection - syphilis reaches the last stage, then it becomes life-threatening. Treatment at this stage can stop the disease from getting worse. Syphilis in this phase is not transmitted.
If syphilis is not treated at this stage, complications can develop which may cause damage to:
- heart
- brain
- blood vessels
- nerves
- bones
- liver
- links
- Cardiovascular syphilis
- Neurosyphilis
- Bones Syphilis
Neurosyphilis
- Headache
- Stiffness in the neck
- Confusion or hearing loss
- Lack of balance
- Weakness
- Dementia
 «Many call syphilis "The great pretender", as it "mimics" symptoms of other diseases»
«Many call syphilis "The great pretender", as it "mimics" symptoms of other diseases»
Congenital Syphilis
- prematurity
- low birth weight
- fetal death
- perinatal death
- deformed bones
- brain and nerve problems such as blindness and deafness
- severe anemia
- jaundice
- meningitis
 «With congenital syphilis, the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, or death of the newborn increases dramatically a few days after birth»
«With congenital syphilis, the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, or death of the newborn increases dramatically a few days after birth»
Syphilis Diagnosis
The diagnosis of syphilis is made by the dermatologist-venereologist with special blood tests, which will confirm the existence of antibodies produced by the body to fight the infection.
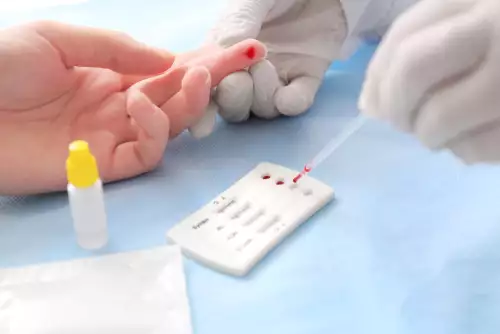
In the early stages of syphilis, a sample may be taken from the sores caused by syphilis and sent to the laboratory for evaluation.
Antibodies produced by the body to fight infection remain in the body for years, so the test can tell if there is a current or past infection.
If the test is positive, the doctor will determine the stage of syphilis by evaluating the test results and taking a complete medical history of the patient.
- the blood
- the wounds or from other damages
- the cerebrospinal fluid
Syphilis & Positive Diagnosis
If the test is positive, the doctor will determine the stage of syphilis by evaluating the test results and taking a complete medical history of the patient.
The next step is to tell your partner(s) that you have been diagnosed with syphilis so that they can also be tested and, if necessary, treated.
This will prevent syphilis from being passed on to other people and your own possible re-infection.
Avoid sexual intercourse for at least a week and until the treatment is complete and you have no sores on your body.
When you start having sex again, don't be afraid to ask your partner about his or her sexual health and, of course, make sure to take protective measures.
 «Even if someone is cured of syphilis, reinfection can occur if they are exposed to the bacteria again»
«Even if someone is cured of syphilis, reinfection can occur if they are exposed to the bacteria again»
Syphilis Treatment
Syphilis can be treated in all stages, but easier in the initial stages.
The main treatment for syphilis is penicillin, while in case of allergy there are alternative antibiotic options.
The treatment most often preferred is an antibiotic called penicillin.
Treated patients should be monitored at regular intervals as determined by the physician. Some patients may need more doses of penicillin, others may become reinfected, etc.
If the infection has occurred within the last year, an injection of penicillin can stop its progression. Otherwise, more doses of the drug may be needed. If someone is allergic to penicillin then an antibiotic will be administered elsewhere.
Side effects of penicillin are very rare and may include fever, headache, nausea, chills, and severe pain, but these symptoms usually do not last more than 24 hours.
The prognosis for most treated patients is good. Conversely, those who do not comply with treatment or delay receiving treatment for syphilis can face serious, often life-threatening conditions.
Syphilis: After Treatment
Syphilis can be treated in all stages, but easier in the initial stages.
After receiving treatment, the patient should:
- Have blood tests done periodically to see if he is responding to treatment.
- Avoid sexual contact until it is proven that the infection has been treated.
- To inform recent sexual partners so that they too can be examined and, if necessary, receive treatment.
- To be tested for infection by other sexually transmitted diseases and the HIV virus, since syphilis wounds bleed easily and thus the HIV virus can enter the body during sexual intercourse.
 «For those who wish to have a child, before trying to conceive, it is mandatory to be tested for infection from sexually transmitted diseases, including syphilis»
«For those who wish to have a child, before trying to conceive, it is mandatory to be tested for infection from sexually transmitted diseases, including syphilis»
Syphilis & Prevention
Reducing the risk!
Condoms prevent syphilis from spreading by preventing contact with any of the sores it causes. Many times, however, the wounds are created in areas not covered by the condom. These sores can transmit the disease of syphilis.
A mutually monogamous long-term relationship also reduces the chances of contracting syphilis.
The greater the number of sexual partners, the greater the risk of exposure to syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases.
Still don't hesitate to talk to your partner about his sex life, including whether he's being tested for sexually transmitted diseases.
 «If you notice unusual rashes, irritations, ulcers or discharge, especially in the genital area, see a dermatologist immediately»
«If you notice unusual rashes, irritations, ulcers or discharge, especially in the genital area, see a dermatologist immediately»
Syphilis: Myths & Truths
Myth #1
Syphilis is a thing of the past.
Fact: CDC (Centers for Disease Control) data show that syphilis cases have increased significantly from 2.1 per 100,000 cases in 2000-2001 to 9΄5 cases per 100,000 in 2017.
Myth #2
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease that affects heterosexual couples.
Truth: Evidence shows that the increase in syphilis cases since 2000 is largely attributable to men who have sex with men. However, in recent years the percentage of men who have sexual contact with women has also increased.
Myth #3
Syphilis is not transmitted through oral sex.
Truth: Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease that is spread during vaginal, anal or oral sex.
Myth #4
Syphilis is easily detected.
Truth: Unfortunately, patients may be infected with the syphilis bacterium and not know it, as the symptoms "hide" in the vagina, anus, under the foreskin, or in the mouth.
Myth #5
Syphilis is an incurable disease.
Truth: Syphilis is treated with antibiotics.
Myth #6
Syphilis is not dangerous.
Truth: If left untreated, syphilis can cause serious health problems, including blindness and permanent neurological damage. It can also prove fatal to the fetus of the infected pregnant woman.
Myth #7
Treatment for syphilis can also reverse the damage that has been done to the body.
Truth: Antibiotics will cure syphilis. It is not certain, however, that he will deal with the damage he has caused to the body.
Myth #8
I've had syphilis, so I won't get it again.
Truth: Just because you've had and been treated successfully for syphilis, it doesn't mean you're protected from the disease. You may become infected again.
Myth #9
I don't have many sexual partners, so I'm not at risk of syphilis.
Truth: You can get syphilis when you are sexually active. The only way to be absolutely sure you won't get syphilis is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex.

Frequent Questions
Is syphilis 100% curable?
How is syphilis transmitted?
Can syphilis be spread by using or touching objects such as the toilet?
Is there a risk of getting syphilis from kissing?
How is the treatment administered?
Bibliography
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534780/
- https://www.who.int/health-topics/syphilis#tab=tab_1
- https://share.upmc.com/
- https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/stdfact-syphilis-detailed.htm
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4622-syphilis
- https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/syphilis-treatment
