HPV Warts
Treatment Duration
30
Suggested Sessions
2-3 times/year
What are HPV warts?
Unsightly and annoying, genital warts owe their existence to HPV, the virus responsible for the most common sexually transmitted infection in the Western world.
Warts are skin growths-lesions on the skin or mucous membranes of the anus, which are caused by the human papillomavirus HPV (Human Papillomavirus).
It is estimated that the vast majority of sexually active individuals will be infected with HPV and develop warts by the age of 45.
 «HPV and warts have nothing to do with HIV and HSV (herpes)»
«HPV and warts have nothing to do with HIV and HSV (herpes)»
Who do HPV Warts affect?
Genital warts affect both men and women. More simply, warts affect anyone who has sexual contact. It seems to be more common in young adults, while there is also a male bias.
It is estimated that most sexually active people will come into contact with one or more types of the virus at some point and develop warts in their lifetime.
HPV Warts & Causes
Of the large family of about 200 types of HPV, about 40 are sexually transmitted, some of which cause warts.
In addition, some of the above types of virus are characterized as high risk, about 14, as they can cause cancer of the genital organs or the oropharyngeal cavity.
Except for the types of viruses that cause warts, most do not cause symptoms.
The viruses that cause genital warts, mainly HPV types 6 and 11, are generally considered low risk.
On the contrary, the high-risk genotypes of the virus, 16 and 28, are responsible according to the World Health Organization for 70% of cervical cancers.
 « Approximately 80% of sexually active individuals will be exposed to HPV at least once in their lifetime»
« Approximately 80% of sexually active individuals will be exposed to HPV at least once in their lifetime»HPV Warts: Risk Factors
Factors that may increase the risk of genital warts infection are:
- Sex without precautions with multiple partners.
- The existence of another sexually transmitted infection.
- When one becomes sexually active early.
- Weak immune system such as from HIV.
HPV warts: How do they get infected?
Genital warts are highly contagious.
They are transmitted mainly through sexual contact, and more specifically:
- With vaginal sex.
- With anal sex.
- With oral sex.
- By touching the genitals without ejaculation.
- By sharing sex toys.
 «Genital warts are spread even when they are not visible»
«Genital warts are spread even when they are not visible»
HPV Warts & Viral Load
Treatment for HPV Warts
When both sexual partners are infected with HPV and have warts, then the corresponding viral load in the couples is also increased.
Successful treatment can reduce viral load as well as transmission. In some cases, however, areas remain where the HPV virus remains latent and can be transmitted, causing new warts.
HPV Warts & Symptoms
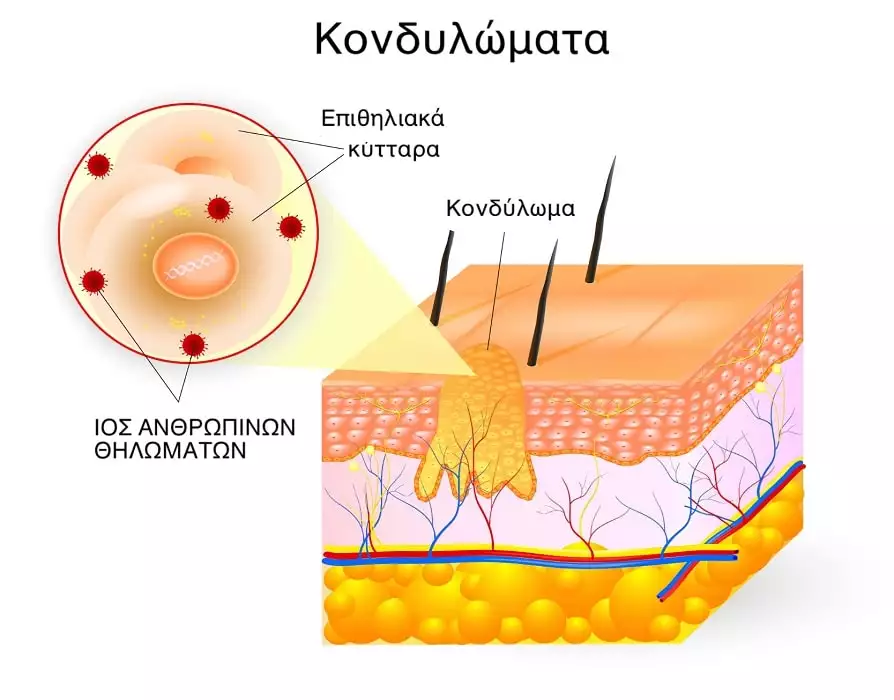
Genital warts are small skin-colored or slightly darker bumps and are often the only symptom of infection.
Skin growths, i.e. warts, can be internal or external, flat and smooth or raised with a rough surface.
Also, the warts can appear individually or as a whole "cluster" that looks like tiny "cauliflowers".
However, many times patients do not show any symptoms.
In other cases the patient may feel:
- itch
- burning sensation
- fret
- pain
- light bleeding
With the naked eye, only acute warts are visible, which are generally benign lesions that do not cause cancer, in contrast to flat warts, which are considered subclinical lesions of the genital system and must be checked immediately and thoroughly with special lenses, strong light and diagnostic tests.
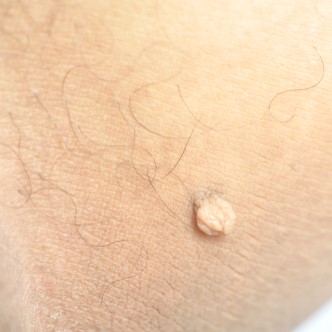 HPV Warts: Pictures
HPV Warts: PicturesYou can see photos of oral, genital and anal warts in men and women so you can identify them on your body or your sexual partner.
HPV Warts: Early Stage
Genital warts come in various sizes and shapes. By checking your body you can spot warts at an early stage and see your doctor before they start to grow and spread.
Observing the area around and inside the vulva and groin for women and the penis, scrotum, groin and thighs for men will usually detect:
- Small lumps - warts, 2-3 mm in the color of the skin that often develop in groups.
- Often there may only be 1 or 2 warts.
- Genital warts often appear in moist areas such as in or around the vagina from the anus and do not cause pain or discomfort.
The time of manifestation of Warts is not specific.
You can be a carrier of the HPV virus but not develop warts.
HPV Warts Men
Genital warts affect both sexes. Men are infected with the HPV virus through vaginal, anal or oral sex, but very often they show no symptoms and the infection clears up on its own.
However, they may show:
Penis Warts
The penis is the common site of infection and appearance of warts in men. HPV is considered to be present subclinically (that is, without symptoms) in a significant percentage of the general population.
Anal Warts
Anal warts affect the area around and inside the anus, as well as the perineal area. These types of warts appear more often in people who have anal sex, while men who have sex with men seem to be more likely to develop cancerous lesions in the area.
Evidence from the medical literature shows a significant increase in recent years in anal intraepithelial neoplasia, that is, the abnormal growth of dysplastic cells in the area of warts.
Throat Warts
High-risk subtypes of HPV can cause a form of throat cancer called oropharyngeal cancer, which appears to be on the rise in recent years.
HPV Warts Women
As in men, genital warts also appear in women who are infected with HPV. The types of virus that cause warts are characterized as low risk in contrast to other high risk strains responsible for the development of cervical cancer.
Vagina Warts
In women, warts may appear inside the vagina, which does not help to identify them.
Vulva Warts
The vulva is a very common area where warts develop.
In both men and women, warts can also appear on the lips, mouth, tongue and throat.
 «When looking for early signs of warts you should keep in mind that warts can appear weeks or even months after infection. Some people who are infected with the virus will never show symptoms»
«When looking for early signs of warts you should keep in mind that warts can appear weeks or even months after infection. Some people who are infected with the virus will never show symptoms»
HPV Warts & Body Areas
The signs of genital warts in men and women are:
- The penis.
- The vagina (and internally) the cervix, the vulva, the labia minora and the labia majora.
- The area of the anus and the rectum.
- The lips, tongue, mouth and throat.
- The groin.
HPV Warts Diagnosis
A key point in the management and treatment of warts is the examination by a specialist dermatologist - venereologist.
Genital warts are often diagnosed only by clinical examination, but they are often found in non-visible places, such as inside the vagina or anus or the mouth and throat.
In this case the necessary tests should be done, so the dermatologist is the right person to direct you for:
- Genital control.
- Rectal examination.
- Oropharyngeal control.
In any case, regular gynecological examinations are important for women, as well as the Pap test or HPV test if needed to detect vaginal or cervical lesions that can cause genital warts or indicate cervical cancer.
Read also...
In addition, if the doctor deems it necessary, he can recommend a more specific examination, the colposcopy, which allows a better overview of the area, with the possibility of performing a biopsy for the warts.
Read also...
An important test for detecting internal warts is also a colposcopy, which is performed when warts are found in the perianal area, in order to determine whether they are also present inside the anus.
 «Visiting the doctor should not be a reason for embarrassment, but should be rushed so that you know exactly what is happening to you and how it is treated»
«Visiting the doctor should not be a reason for embarrassment, but should be rushed so that you know exactly what is happening to you and how it is treated»
They may not be HPV Warts
Visiting the specialist doctor who is the venerologist dermatologist is necessary when you notice a small lump or a skin growth in the genital area, as it may not be genital warts but other skin lesions such as:
- Genital herpes caused by the herpes simplex virus.
- Red painful pimples from folliculitis on pubic hair.
- Pimples, like those present on the rest of the body, which may have a hormonal etiology.
- Cutaneous papillomas, small, harmless, i.e. skin bumps.
- The well-known moles, which appear all over the body including the genitals.
- You are relieved of any discomfort, pain or itching.
- You know your skin growths are warts and nothing else.
- Warts that are difficult to keep clean are removed.
- Precancerous lesions
- Cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina and anus.
- Genital warts.
HPV Warts Treatment
First of all, we should note that we treat warts and not HPV, which remains in the body.
The treatment that the doctor will recommend for warts is not the same for every patient. It depends on factors such as the size and distribution of the genital warts but also the overall state of his health.
For warts, there are treatments that are available and only done in the doctor's office, but also treatments that we can apply at home, or a combination of the above, always with the guidance of the doctor.
Topical Treatment
The doctor may recommend topical creams/ointments for external genital warts, which destroy cells in the area that may be infected, reducing the viral load before they develop into warts.
Laser CO2 Treatment
CO2 laser treatment for warts is a modern treatment, which specifically fights skin lesions - warts, both external and internal. The procedure is performed with the application of an anesthetic cream, which makes it well tolerated.
For warts located in internal parts of the body, Laser sublimation can be applied during colposcopy and rectoscopy with the help of a microscope.
Diathermocoagulation
This is one of the most common removal methods for warts.
It is a relatively easy procedure, during which a noble gas is administered on the warts, cauterizing them. It has a small depth of injury, therefore less chance of complications.
Cryocoagulation
With the sudden cooling and thawing of the lesions, the cells are killed, resulting in the warts "falling off".
Cryocoagulation is a relatively painless procedure to treat warts, during which there is usually a slight burning sensation.
However, there is the possibility of scarring and, compared to the other treatments, it shows a higher number of recurrences. It usually takes 3-4 repetitions of the treatment to eliminate the warts with an interval of 2-3 weeks.
Surgical Removal
This is a method that is chosen less often since it is indicated for cases where the warts are very developed, their total number is large and they do not respond to other treatments.
With appropriate treatment:
 «The treatment removes the warts, but not the HPV virus that causes them from the body»
«The treatment removes the warts, but not the HPV virus that causes them from the body»
HPV Warts Prevention
HPV Vaccine
The vaccine against the HPV virus is an important means of medical prevention to limit the consequences of the virus, i.e. the appearance of warts, in high-risk groups as well as in the general population.
In our country, it is recommended through the National Program of Vaccination of Adolescents and Children from the age of 9, even completely isolating boys for the first time.
It is also recommended in the National Adult Immunization Program and for adults up to 26 years of age who belong to high-risk groups such as men who have sex with men.
HPV vaccines are not recommended during pregnancy, however it is not necessary to take a pregnancy test before starting the vaccination. In the event that pregnancy is detected, after the administration of the vaccine, it is not recommended to stop it, but the vaccination is completed after its completion.
The vaccine against HPV includes 9 types of the virus, the diseases they cause are:
Condom & HPV Warts
Using a condom correctly every time you have sex will reduce but not eliminate your chances of getting infected with HPV and developing warts, as it can infect areas not covered by the condom.
 Condoms & HPV
Condoms & HPV
Talk openly with your partner about sexual health issues and of course let them know if you are dealing with HPV infection and warts.
HPV Warts: Myths & Truths
Μyth #1
Genital warts are a sign of cancer.
Truth: Genital warts are not caused by the types of viruses that cause cancers like cervical. However, if you have warts, you may have been infected with another HPV virus, so the examination by the specialist doctor is imperative.
Μyth #2
Men and boys do not need to get the HPV vaccine.
Truth: HPV affects men and women equally.
Μyth #3
People who have casual sex are infected with HPV and warts.
Truth: People who have different sexual partners are actually more likely to get a sexually transmitted disease, including HPV. However, this does not condemn them since any sexually active person can be infected with HPV.
Myth #4
HPV infections are not serious in men.
Truth: Infection with HPV strains can cause penile, anal, and throat cancer in men.
Myth #5
I always use a condom, so I'm not at risk for HPV and warts.
Truth: Condoms, when used correctly, are very effective against sexually transmitted diseases. But they are less protective against sexually transmitted diseases such as HPV and herpes. So the condom does not fully protect you from HPV and warts.
Myth #6
HPV and warts do not affect the LGTB community.
Truth: HPV does not discriminate against gender, sexual orientation and preferences. You might discover him along the way.
What does HPV Warts mean for my relationship?
Sexually transmitted diseases are a point of friction for relationships between partners, testing their trust and endurance. However, with HPV things are different, as the diagnosis of infection does not necessarily mean infidelity, since the virus can remain dormant in the body for a long time before symptoms and warts appear.
So you cannot know for sure when and from whom you were infected with the virus, although when you in turn transmitted it.
A diagnosis of HPV therefore means that at some point in the past you were infected with the virus.
HPV in Numbers
HPV is responsible for 4.5% of all cancers worldwide.
HPV is involved in almost all cases of cervical cancer, as well as 90% of cancers in the anal area.
2.5% of cancers in Europe are related to HPV, which translates to 67,500 per year
In Europe in 2018, 26,000 deaths in Europe were linked to cervical cancer.

Frequent Questions
Pimples like pimples appeared on my genitals. Could it be hpv warts?
For starters, you shouldn't panic. You should see a dermatologist to properly diagnose the condition. If the "pimples" are itchy, painful, stinging or secrete pus, then they are definitely not warts, however, a visit to the dermatologist is required since there may be an infection from another sexually transmitted disease.
How to identify genital hpv warts?
Checking the genital area you may notice small skin bumps, skin-colored or lighter pink, usually painless. It could be warts. For this you should visit your doctor.
How do HPV warts stick?
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted disease and are almost always transmitted through vaginal, anal and oral sex. They also don't need to be visible to be transmitted.
What do warts look like?
Warts can be very small skin growths on or around the genitals They can be flat or have a stalk. In addition, you may discover them individually or in clusters.
Is there a chance that I will get hpv warts more than once?
HPV is not curable. So genital warts can appear again and again.
How do hpv warts go away?
Most of the time you will need some treatment to get rid of genital warts, which can be local, some procedure in the office always by the qualified doctor.
Bibliography
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441884
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3140331
- https://www.zavamed.com/uk/early-signs-of-genital-warts.html#:~:text=The%20main%20symptom%20of%20the,Itching%20or%20inflammation
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/condyloma
- https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/genital-warts
- https://www.europeancancer.org/2-standard/111-the-impact-of-hpv